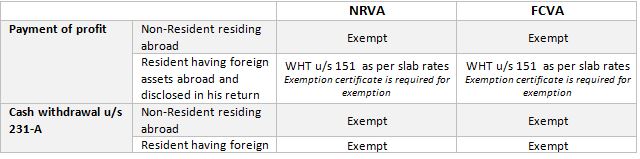
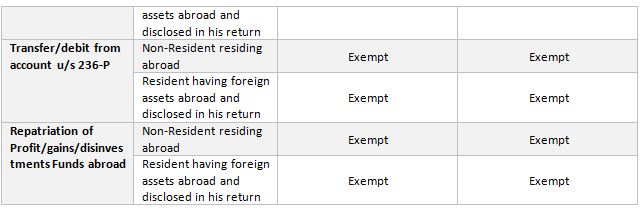
WhatsApp Message
WhatsApp Message
Pakistan levies tax on its residents on their worldwide income. A non-resident individual is taxed only on Pakistan-source income, including income received or deemed to be received in Pakistan or deemed to accrue or arise in Pakistan.
The following tax rates apply where income of the individual from salary exceeds 75% of taxable income. (see the Salary Tax Calculator in the software download section.)
| Taxable income (PKR) | Tax on column 1 (PKR) | Tax on excess (%) | |
| Over (column 1) | Not over | ||
| 0 | 600,000 | 0 | |
| 600,001 | 1,200,000 | 2.50% | |
| 1,200,001 | 2,400,000 | 15,000 | 12.50% |
| 2,400,001 | 3,600,000 | 1,65,000 | 20% |
| 3,600,001 | 6,000,000 | 405,000 | 25% |
| 6,000,001 | 12,000,000 | 1,005,000 | 32.50% |
| 12,000,001 | 2,955,000 | 35% | |
The following tax rates are applicable in other cases (for individuals and association of persons):
| Taxable income (PKR) | Tax on column 1 (PKR) | Tax on excess (%) | |
| Over (column 1) | Not over | ||
| 0 | 600,000 | 0 | |
| 600,001 | 800,000 | 5% | |
| 800,001 | 1,200,000 | 10,000 | 12.50% |
| 1,200,001 | 2,400,000 | 60,000 | 17.50% |
| 2,400,001 | 3,000,000 | 270,000 | 22.50% |
| 3,000,001 | 4,000,000 | 405,000 | 27.50% |
| 4,000,001 | 6,000,000 | 680,000 | 32.50% |
| 6,000,001 | 1,330,000 | 35% | |
A person is resident in Pakistan for income tax purposes:
Taxable income is calculated under five different types of income, as follows:
Employee’s gross salary is Pakistan-source income and taxable in Pakistan if it is earned from employment exercised in Pakistan or if it is paid by or on behalf of the federal government, a provincial government, or a local authority.
Salary is the amount received by an employee from employment, whether of a revenue or capital nature. It includes leave pay, payment in lieu of leave, overtime, bonuses, commissions, fees, gratuities, work condition supplements, monetary and non-monetary perquisites, any allowance except those granted to meet expenses wholly and necessarily incurred in the performance of the employee’s duties of employment, profits in lieu of or in addition to salary, pensions, annuities, and tax reimbursement. In addition, amounts or perquisites paid or provided by an associate of the employer, a third-party under an arrangement with the employer or associate of the employer, a past employer or a prospective employer, or payments to an associate of the employee are also to be considered as salary.
Salaried individuals employed by the oil exploration and production sector are exempt from tax for a period of three years from the date of their arrival in Pakistan, though such exemption has been challenged by the department before higher courts in certain cases.
Diplomats and individuals entitled to United Nations (Privileges and Immunities) Act 1948 are exempt from tax on their salaries.
Income from property derived by an individual is a separate block of income and taxable on a gross basis (without deduction of any expenses). Income from property shall be subject to tax as follows: (see the Tax Calculator on Property Income in the software download section.)
| Taxable income (PKR) | Tax on column 1 (PKR) | Tax on excess (%) | |
| Over (column 1) | Not over | ||
| 0 | 300,000 | 0 | |
| 300,000 | 600,000 | 5 | |
| 600,000 | 2,000,000 | 15,000 | 10 |
| 2,000,000 | 155,000 | 25 | |
Capital gains on the sale, exchange, or transfer of movable capital assets are taxable. Capital gain on the sale of immovable property is subject to tax, depending upon the amount of gain and holding period in the manner tabulated below:
|
Sr.no |
Holding period |
Rate of Tax (%) |
||
|
Open Plots |
Constructed property |
Flats |
||
|
1 |
Where the holding period does not exceed one year |
15 |
15 |
15 |
|
2 |
Where the holding period exceeds one year but does not exceed two years |
12.5 |
10 |
7.5 |
|
3 |
Where the holding period exceeds two years but does not exceed three years |
10 |
7.5 |
0 |
|
4 |
Where the holding period exceeds three years but does not exceed four years |
7.5 |
5 |
0 |
|
5 |
Where the holding period exceeds four years but does not exceed five years |
5 |
0 |
0 |
|
6 |
Where the holding period exceeds five years but does not exceed six years |
2.5 |
0 |
0 |
|
7 |
Where the holding period exceeds six years |
0 |
0 |
0 |
Capital gains relating to disposal of immovable properties situated outside Pakistan will be taxed at applicable rates irrespective of holding period.
Purchase of immovable property exceeding PKR 5 million and any other asset exceeding PKR 1 million by way of other than a banking channel shall not be considered as an eligible cost for the purpose of computation of capital gain as well as the related asset shall not be considered as an eligible depreciable asset. Moreover, such action would also invite penal consequences for the purchaser.
Gain on disposal of listed securities (that was previously chargeable to tax @ 12.5% irrespective of the holding period) shall now be subject to revised tax rates based on holding period, for securities purchased post July 1, 2022. The revised rates are as under:
|
Holding period |
Tax (%) |
|
Less than one year |
15 |
|
From one year to two year |
12.5 |
|
From two years to three years |
10 |
|
From three years to four years |
7.5 |
|
From four years to five years |
5 |
|
From five years to six years |
2.5 |
|
More than six years |
0 |
Loss on disposal of listed and other securities could earlier only be set off against capital gains (and not allowed to be carried forward). From tax year 2019 and onwards, such loss is now allowed to be carried forward and set off against future capital gains on such securities, up to a maximum of three tax years.
Foreign companies (not having PE in Pakistan) and non-resident individuals investing in Pakistan in debt instruments and government securities through SCRAs and RDAs are subject to a blanket 10% WHT rate on capital gain arising on disposal of these debt instruments and government securities. This deduction shall be full and final discharge of their tax liability.
Dividend income received from a company (including mutual funds and real estate investment trusts [REITs], etc.) is generally subject to final tax at the rate of 15%; however, a different rate would apply in the following cases:
Significant exemptions available under salary income are as follows:
Any foreign-source salary received by a resident individual is exempt from tax in Pakistan if the individual has paid foreign income tax in respect of that salary.
Where a resident taxpayer derives foreign-source income chargeable to tax in Pakistan, in respect of which the taxpayer has paid foreign tax, the taxpayer is allowed a credit of an amount equal to the lesser of the foreign income tax paid or the Pakistan tax payable in respect of the income.
Foreign-source income of a resident who is not a citizen of Pakistan is exempt if the individual is resident only by virtue of employment and one’s presence in Pakistan does not exceed three years. This exemption does not apply in the case of income from a business established in Pakistan and foreign-source income that is brought into or received in Pakistan.
Pakistan has executed tax treaties with more than 66 countries (see the Withholding taxes section in the Corporate tax summary for a list of countries with which Pakistan has a tax treaty). These conventions aim to eliminate double taxation of income or gains arising in one territory and paid to residents of another territory. The provisions of the tax treaties take precedence over the tax laws applicable in Pakistan with respect to taxation of Pakistan-source income of a non-resident person (subject to certain restrictions now introduced in law; for detail, please refer to the Other issues section in the Corporate tax summary). Most of the treaties are based on the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) Model Tax Convention.
The tax year is 1 July through 30 June.
An individual is required to file a return of income with the tax authorities on a fiscal year basis (1 July through 30 June). Filing of a revised return requires prior approval of the Commissioner, subject to certain limitations and conditions. The Commissioner is now also empowered to grant approval for revision of a return for a bona fide omission or wrong statement.
Every resident taxpayer filing a return of income is required to file a wealth statement (in the prescribed format) along with the return of income. The Commissioner can also require any person to furnish the said statement. For revision of a wealth statement, an intimation has to be filed with the Commissioner, who is empowered to disallow/disregard such revision in case he/she is of the view that the same has not been made for correction of bona fide errors or omissions. A taxpayer has been allowed to make revision of a wealth statement up to a period of five years.
Every resident taxpayer being an individual and having foreign income equal to or in excess of 10,000 United States dollars (USD) or having foreign assets with a value of USD 100,000 or more is now also required to file a separate statement of foreign income and foreign assets in a prescribed format. The Commissioner can also require any person to furnish such statement.
All individuals (including salaried persons) are required to file their return/wealth statement for the year ended 30 June by 30 September. Late filing shall be liable to penalty proceedings.
Persons whose income was subject to the final tax regime were previously required to file a statement prescribed in the law in lieu of a return of income; however, such requirement has now been omitted. The FBR is to prescribe returns for different classes of income or persons, including those covered by the final tax regime.
Income tax is withheld from salaries by the employer. The amount to be withheld is determined by applying to the salary the average rate of tax on the estimated income of the employee for the fiscal year.
Advance tax is payable by an individual (other than a salaried individual) in four instalments if the latest assessed taxable income is in excess of PKR 1 million.
An audit of the tax return filed by a taxpayer can be conducted by the tax authorities within five years of the end of the financial year in which the return is filed. A person, whose income tax affairs have been audited in any preceding four tax years, he shall have immunity from selection of audit. However, amendment proceedings may be initiated other than by way of selection of audit.
Tax authorities can probe into the source of unexplained offshore assets and foreign source income irrespective of any time limitation.
The time period to pass an amendment order is 180 days from the issuance of show cause notice.
The tax authorities mainly focus their attention on taxpayers other than salaried individuals.